What Is A Recession & How Could It Affect You?

What is a recession?
An economic recession is a country’s low GDP, or negative GDP growth for two or more consecutive quarters. Most of the world’s recessions have been short-lived.
In the first three months of this year, the US GDP fell at an annualized rate of 1.6%. And the US Department of Commerce announced that GDP fell again in the second quarter, at an annualized rate of 0.9%.
However, the definition that recession is a decline in gross domestic product (GDP) for six months or more, is objected by many economists.
The first argument relates to the definition, which does not take into account changes that occur in several indicators, including changes in the unemployment rate and consumer confidence.
The second consideration is that using a quarter makes it difficult to determine when a recession begins or ends, i.e. a ten-month recession cannot be monitored.
There’s another approach to define recession, by which it occurs after economic activity, including employment, industrial production, real income, and retail trade sales; reaches its peak and then begins to decline, and the recession continues until economic activity recovers and begins to rise.
The effects of the recession can be seen in the significant decline in economic activity for several months, which reflects a decrease in the gross domestic product and real income of the state, in the increase in unemployment, in industrial production, in retail sales, and in turmoil in stock markets.
When does a recession begin?
A recession begins after economic activity reaches its peak, and ends after the economy reaches its lowest stage of growth. After that, the economy begins a new phase in which it climbs back to the top in what is known as economic growth.
The period of recession is accompanied by a decline in general economic activity, an increase in the number of unemployed people, a decrease in the volume of investments and company profits, and the recession may also be accompanied by a significant drop in prices, i.e. a decrease in the rate of inflation, and it may also be accompanied by a significant rise in the rate of inflation.
A recession for a prolonged period is called an economic depression, and if it is severe, it is described as an economic collapse.
Are we in a recession?
Economic recession is one of the components of the overall economy, which means that this phenomenon or problem generally affects the economy as a whole, thus affecting unemployment rates, the purchasing power of currencies, the ability of the country’s economy to grow properly and correctly, in addition to many other aspects.
In times of economic slowdown that we live in today, everyone suffers, and more burdens are laid on families, companies and governments. Also, in those periods, everyone worries about losing their job, and fears emerge about not being able to pay bills or bear the load of daily life.
So what is a recession? What are its causes and influencing factors? And what does inflation have to do with it? All these questions are what we’ll be tackling in this blog.
What caused the recession?
Usually the cause of a recession is that production exceeds consumption, which leads to a depression. Goods and prices fall, so it is difficult for producers to sell inventory, thus the production rate decreases.
As for the recession we are witnessing nowadays, we should mention that over the past 18 months, several factors have combined to create such a mix for the global economy.
The United States has over-stimulated its economy in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to inflation not just within its borders but also outside it, to Canada, Germany and Britain, where the picture of GDP figures is bleak.
Consumers’ insatiable demand for goods has led to Strengthening global supply chains. On the other hand, China’s attempts to eliminate the Corona epidemic through closures have also exacerbated these problems.
In response to the ensuing inflation, four-fifths of central banks worldwide have raised interest rates by an average of 1.5 percentage points so far this year, sending stock markets into a tailspin.
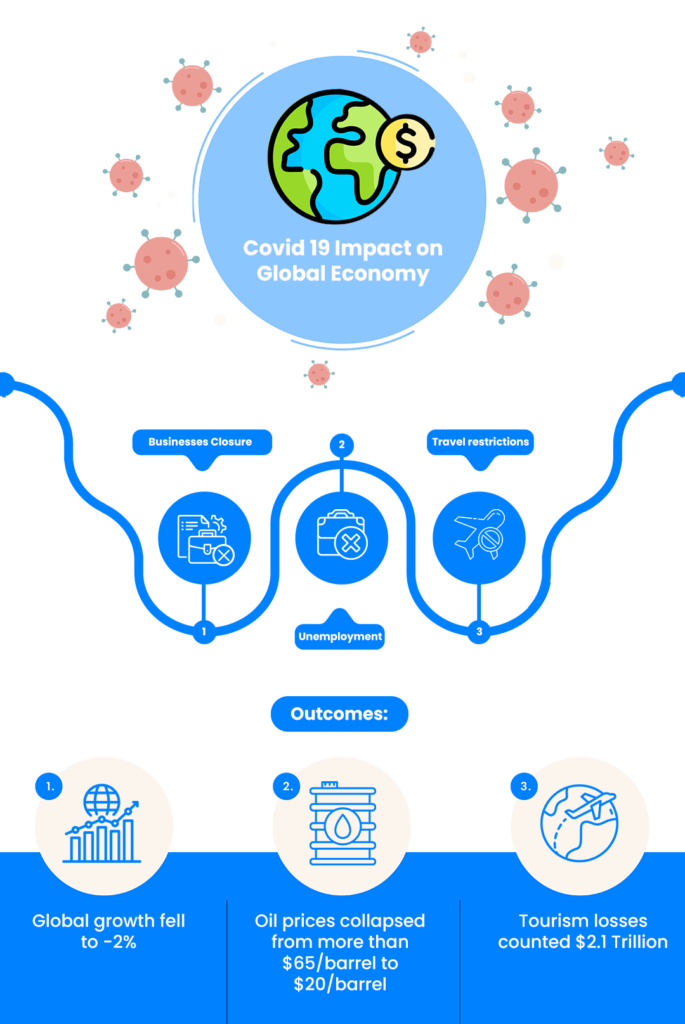
World Economic growth projection
How does the recession affect the world?
The current economic status is putting the United States in the spotlight, the largest economy in the globe and the strongest currency that dominates the world.
Today the global economy has entered the tunnel of stagflation, as it is a condition that the world has only witnessed once previously, and it lasted from the mid-sixties until the beginning of the eighties, and it is a situation in which it the inflation rate in the United States and the rest of the Western countries has risen to more than 10% as a minimum.
Hence, these are rates that have not occurred again since 1982 until the current year 2022.
Another factor is the rise in oil prices. In the beginning of the seventies of the last century, the increasing prices of oil had a major role in the case of inflationary stagnation in the West, and currently the same reason is playing a major role, although the first reason was the Corona pandemic, whose outbreak in early 2020 was tantamount to pulling the main power plug from the global economy, adding to it the outbreak of war in Ukraine.
With the inflation rate in the United States rising to unprecedented levels and the US Central Bank taking successive decisions to raise the interest rate, global markets are in a state of extreme panic, which was already present, but was exacerbated by the American decision.
In brief, the impacts of the recession can be summarized as follows:
1- Expansion of bankrupt companies due to low demand
2- The fall in aggregate demand due to the decline in investment and consumption
3- The decline in the value of assets due to the decline in competition and speculation
4- High unemployment rates due to layoffs
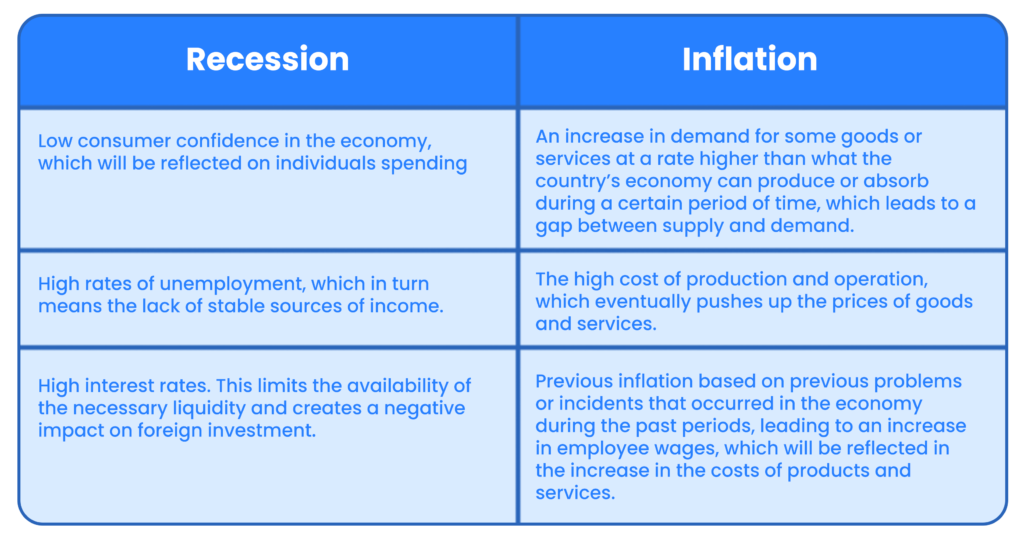
Recession vs Inflation
As mentioned previously, the concept of recession refers to a significant decline in the economic activity of a particular country during a period, specified by economists over two consecutive quarters of the same year. It can be noted that recession is less severe or harsh on the economy than economic depression.
While the concept of inflation refers to the decrease in the purchasing power of a country’s currency over time, and through this it is noted that there is a general rise in commodity prices as a result of inflation, which means that individuals will buy a smaller group of products with the same previously paid value of the currency, this Inflation is a reflection of the concept of economic deflation.
Bottom Line
It seems that there are many challenges that impede achieving a good recovery for the global economy after the Corona pandemic and its impact on the economies, in addition to the repercussions of the Russian war on Ukraine, in terms of fueling the energy and food crises, and the subsequent price hikes and a threat to supplies in the international market.
However, the experience of such economic situations has proven to find its way towards a solution. Just as the 2008 financial crisis was followed by an economic relief, investors are eyeing on a similar recovery with the entrance of 2023.